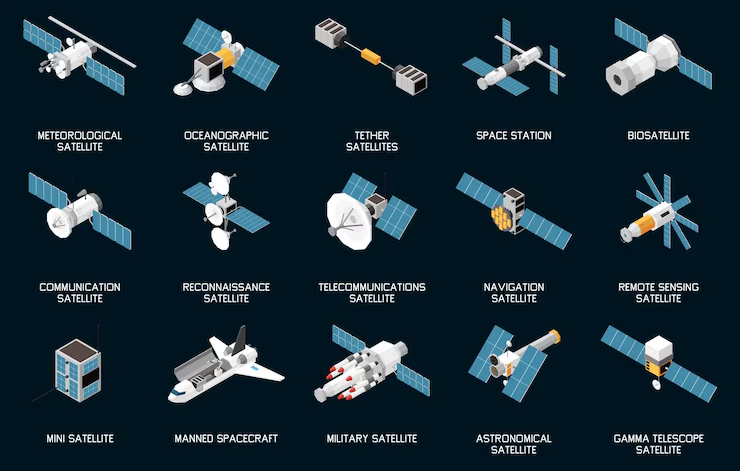
In the modern era of space technology, Sattelitters play an indispensable role in shaping how we communicate, navigate, monitor weather, and even conduct military operations. With thousands of these advanced machines floating in Earth’s orbit, it’s essential to understand the different types and their unique functions. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a student, or just curious about space innovation, this guide breaks down everything you need to know about the different kinds of sattelitters orbiting our planet.
What Exactly Are Sattelitters?
Before diving into the types, let’s clarify the term sattelitters. While it may appear as a variation of “satellites,” sattelitters commonly refers to all man-made objects placed into orbit for specific scientific, commercial, or defense purposes. These machines are launched into space to perform tasks that would be difficult or impossible from Earth’s surface.
In the United States, the demand for sattelitters continues to grow with rising investment in communication, navigation, space exploration, and military surveillance. Now, let’s explore the different kinds of sattelitters operating above us.
1. Communication Sattelitters
These are perhaps the most well-known kind of sattelitters. Communication sattelitters relay telephone, television, radio, and internet signals across the globe.
How They Work:
Communication sattelitters are placed in geostationary orbit—about 22,300 miles above the Earth—so they appear stationary from the ground. This helps them provide uninterrupted signals to large areas.
USA Focus:
Companies like SpaceX, HughesNet, and Viasat rely heavily on communication sattelitters to deliver high-speed internet across rural America, especially where cable infrastructure is lacking.
2. Weather Sattelitters
Weather sattelitters help meteorologists monitor atmospheric patterns, forecast storms, track hurricanes, and analyze climate changes.
Key Features:
-
They capture high-resolution images of cloud movements.
-
They measure atmospheric temperature, humidity, and wind.
USA Usage:
Agencies like NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) use weather sattelitters like GOES-16 and GOES-17 to improve forecasting accuracy and disaster preparedness throughout the country.
3. Navigation Sattelitters
Navigation sattelitters power systems like GPS (Global Positioning System) which we use for driving directions, air travel, shipping logistics, and more.
Benefits:
-
Real-time location tracking.
-
Accurate global positioning data.
Strategic Role:
The U.S. Department of Defense originally developed GPS, and now GPS sattelitters are critical to everything from smartphone apps to emergency services across the nation.
4. Earth Observation Sattelitters
These sattelitters observe the Earth’s surface to collect data related to agriculture, deforestation, pollution, urban development, and natural disasters.
Applications:
-
Monitoring wildfires and floods.
-
Crop analysis and land mapping.
Government Use:
Programs like NASA’s Landsat and USGS’s satellite systems provide vital Earth observation data to support environmental policy, scientific research, and climate action in the U.S.
5. Military & Spy Sattelitters
These sattelitters are designed for national security, surveillance, missile tracking, and battlefield communication.
Functions:
-
Monitor enemy movements.
-
Provide encrypted communications.
-
Support missile early-warning systems.
National Defense:
The U.S. Space Force manages and protects a wide array of military sattelitters crucial to the nation’s defense strategy.
6. Scientific & Space Exploration Sattelitters
These specialized sattelitters are launched to explore the solar system, study cosmic phenomena, or support human missions in space.
Missions:
-
Telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope.
-
Mars orbiters and interplanetary probes.
Contributions:
NASA leads the way with sattelitters designed for deep space research, helping scientists explore new planets, stars, and galaxies while boosting America’s global leadership in space exploration.
7. CubeSats and NanoSattelitters
With the rise of private space companies and universities, CubeSats and other small-scale sattelitters are becoming more common.
Features:
-
Lightweight and cost-effective.
-
Used for experiments, testing technologies, or short-term missions.
Innovation & Education:
Institutions like MIT and Stanford University, along with startups like Planet Labs, are revolutionizing sattelitter use in the U.S. by launching fleets of these mini-machines.
The Future of Sattelitters in the U.S.
With the rapid growth of the U.S. space sector, especially led by companies like SpaceX, Amazon’s Project Kuiper, and OneWeb, the number of sattelitters will only increase. Innovations like AI-integrated sattelitters, space-based 5G, and autonomous observation systems are reshaping industries and redefining global connectivity.
Final Thoughts
Sattelitters are more than just machines floating in space—they are the invisible force behind modern life. From helping us make a call to predicting life-threatening storms, sattelitters have become essential tools for progress and safety. As the United States continues to invest in space technology, the scope and impact of these sattelitters will only grow.
Whether you’re a business owner looking to tap into satellite tech, a student exploring careers in aerospace, or a curious reader—understanding the kinds of sattelitters and their purposes opens up a whole new universe of possibilities.